Smart City Pillars
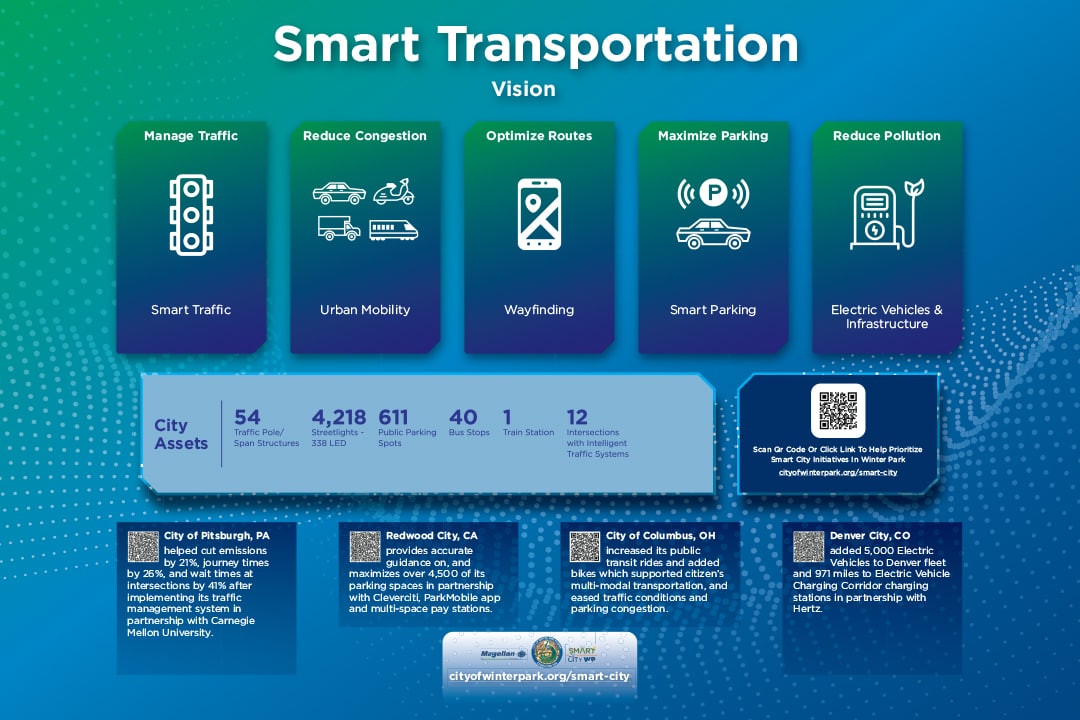
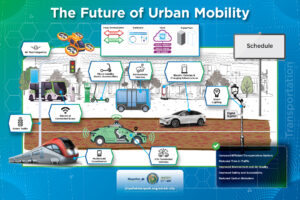
The goal of a smart transportation strategy is to ensure the smooth flow of traffic through the city (and region) and to reduce the time to find parking in the central business district. An intelligent (Smart) transportation systems measures, monitors, and controls the flow of traffic through the city to reduce congestion, optimize routes, detect accidents, and avoid idling pollution. Smart parking identifies open spaces and directs drivers to them.
= The city has implemented some of these features.
= The city will consider implementing these features.
- Air Taxi Integration
Air taxi integration refers to the process of integrating and incorporating air taxi services into existing transportation systems and urban environments. Air taxis, also known as urban air mobility vehicles or electric vertical takeoff and landing (eVTOL) aircraft, are small, electric-powered aircraft designed to transport passengers within urban or suburban areas. - Autonomous Vehicles
Autonomous vehicles, also known as self-driving cars or driverless vehicles, are vehicles equipped with advanced technologies that can operate without human intervention. These vehicles use various sensors, cameras, radar, lidar, and artificial intelligence algorithms to perceive their surroundings, make decisions, and navigate autonomously. - Drone Integration
Drone integration refers to the incorporation of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), commonly known as drones, into existing systems, processes, and industries to enhance operations and provide new services. Drone integration involves the seamless integration of drones with other technologies, regulations, and workflows to ensure safe and efficient operations. - Electric Vehicle Infrastructure
Refers to the network of charging station, equipment and technologies necessary to support the charging and operations of electric vehicles. - Micro-mobility
Transportation modes and services that involve lightweight, often small-scale vehicles for short-distance travel within urban areas, providing efficient, convenient and environmentally friendly transportation options for individuals or small groups. - Multimodal Coordination
The integration and coordination of different transportation modes and services to provide seamless, efficient, and sustainable mobility options for individuals and goods. - Smart Parking
Smart parking refers to a parking system that utilizes advanced technologies to improve the efficiency, convenience, and management of parking spaces in urban areas. - Smart Traffic
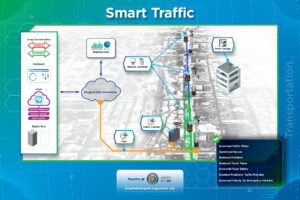
Smart traffic, also known as intelligent traffic management or intelligent transportation systems (ITS), refers to the application of advanced technologies to monitor, analyze, and manage traffic flow on road networks. The goal of smart traffic systems is to improve road safety, optimize traffic efficiency, reduce congestion, and enhance the overall transportation experience. - Smart Vehicles (Public Safety)
Smart public safety vehicles, also known as intelligent emergency response vehicles, leverage advanced technologies to enhance their capabilities and improve public safety operations. These vehicles integrate various technologies and systems to improve communication, data collection, situational awareness, and response times in emergency situations. - Urban Mobility
Urban mobility refers to the movement of people and goods within urban areas and encompasses various modes of transportation and mobility services. - V2X (Vehicle-to-Everything) Communications
Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) communications refers to the exchange of information between vehicles and their surroundings, including other vehicles, infrastructure, pedestrians, and networks. It is a key component of intelligent transportation systems (ITS) and aims to enhance road safety, improve traffic efficiency, and enable new vehicle applications and services. - Wayfinding
Wayfinding refers to the process of navigating and orienting oneself within an environment, such as a building, campus, or city, by using visual cues, signage, maps, and other informational resources.
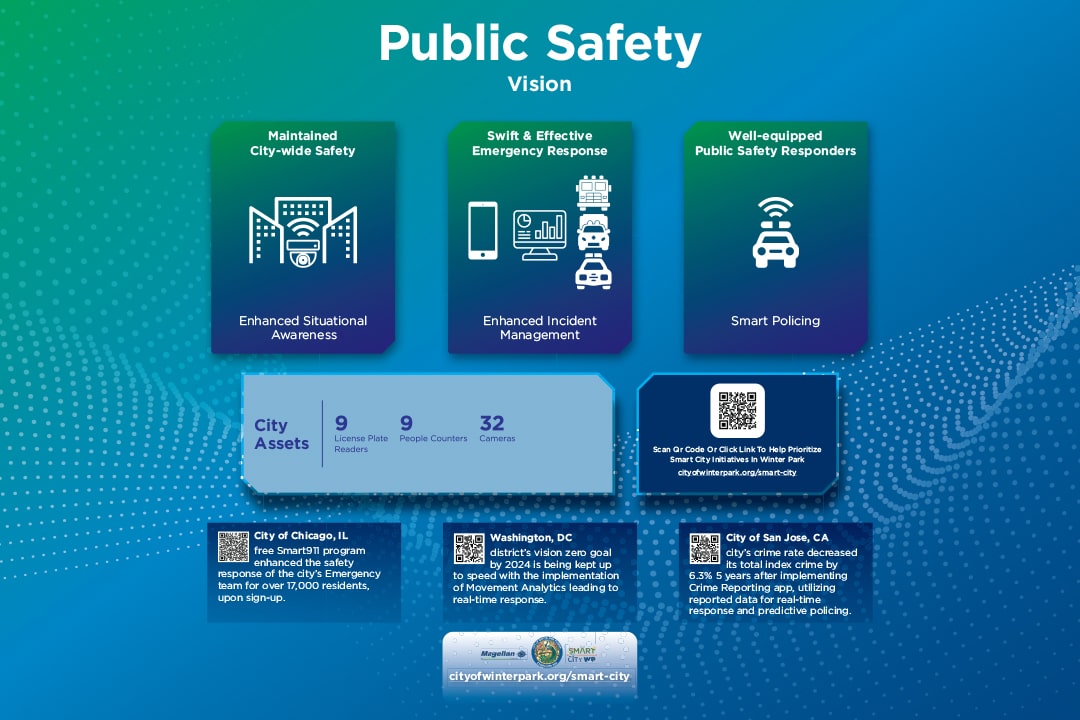
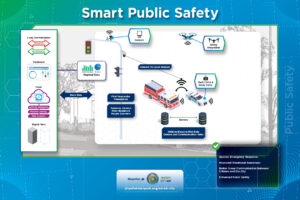
The goal of a smart public safety strategy is to ensure safety of residents, business owners and visitors throughout the city (and region) and to
reduce crimes and improve response times to incidents.
= The city has implemented some of these features.
= The city will consider implementing these features.
- Body Cameras
Body cameras are small recording devices typically worn by law enforcement officers or other professionals to capture audio and video footage of their interactions. Body cameras are designed to provide an objective record of events and enhance transparency, accountability, and trust in public safety operations. - Dash Cameras
Dash cameras are deployed on vehicles to improve situational awareness, after-incident documentation, and transparency. - First Responder Preemption
First Responder Preemption a system that allows emergency vehicles, such as ambulances, fire trucks, and police cars, to control traffic signals to ensure their safe and efficient passage during emergencies. - License Plate Readers
License Plate Readers are specialized devices that can accurately capture license plate that can assist in capturing speed violators and other vehicles tied to a crime. - People Counters
People counters are specialized devices that count the number of people passing by a given location. - Public Cameras
Public cameras have many uses including smart traffic, smart parking and public safety while being respectful of citizens’ rights to privacy. - Smart Vehicles (Public Safety)
Smart public safety vehicles, also known as intelligent emergency response vehicles, leverage advanced technologies to enhance their capabilities and improve public safety operations. These vehicles integrate various technologies and systems to improve communication, data collection, situational awareness, and response times in emergency situations.
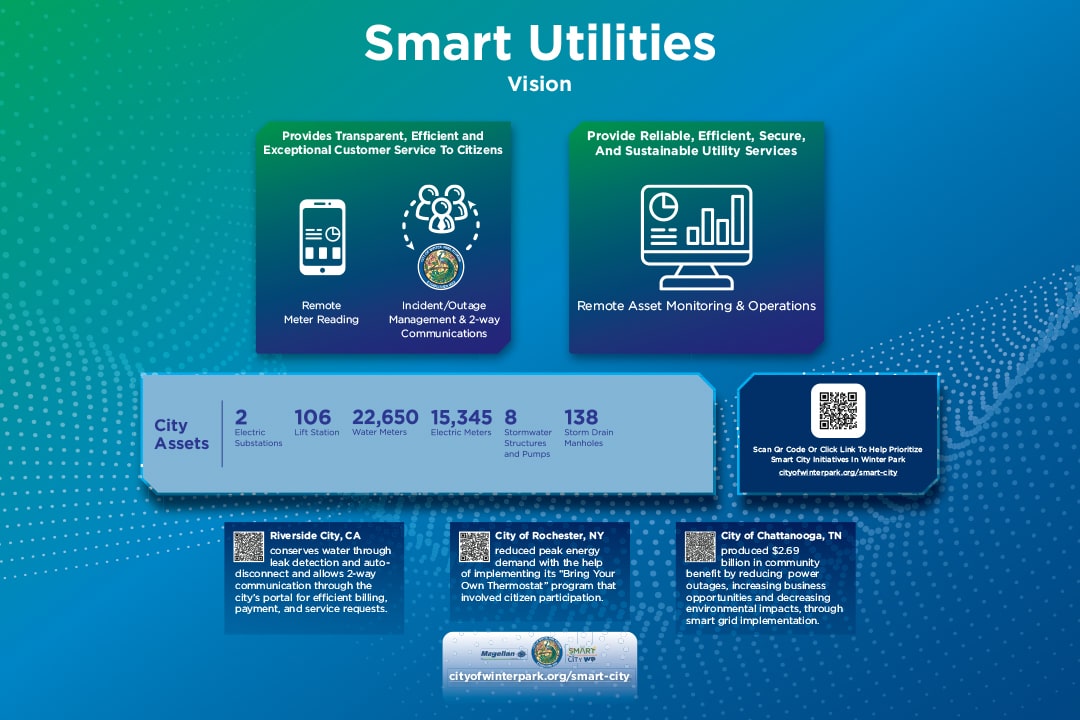
The goal of a smart utilities strategy is to provide Winter Park citizens reliable, transparent, efficient and secure water and electric utility services.
= The city has implemented some of these features.
= The city will consider implementing these features.
- People Counters
People counters are specialized devices that count the number of people passing by a given location. - Remote Payments
Financial transactions that are conducted electronically between two parties who are not physically present at the same location. - Smart Curb Management
Smart Curb Management refers to the use of technology and data-driven solutions to optimize and efficiently manage curbside space in urban areas. - Smart Lighting
Smart lighting refers to an intelligent lighting system that utilizes advanced technologies, such as sensors, wireless connectivity, and automation, to provide enhanced control, energy efficiency, and convenience in lighting applications. - Soil Sensors & Smart Irrigation
Soil sensors and smart irrigation systems are components of an intelligent landscaping approach that leverages technology to optimize water usage and promote efficient plant growth, reducing water waste and improving overall irrigation efficiency. - Stormwater Flow Meter
A stormwater flow meter is a device used to measure the volume and rate of stormwater runoff or the flow of water in stormwater drainage systems. It is a critical component in stormwater management and helps monitor and analyze the flow of water during rainfall events. - Water Analysis Devices
Water analysis devices are instruments or tools used to measure and analyze various parameters and characteristics of water samples. - Water Level Monitoring
Water level monitoring refers to the process of measuring and tracking the water levels in various water bodies, such as rivers, lakes, reservoirs, groundwater wells, and tanks. It is an important aspect of water resource management, flood forecasting, and environmental monitoring. - Water Quality Monitoring
Water quality monitoring involves the systematic assessment and analysis of various physical, chemical, and biological parameters to evaluate the health and safety of water sources. It is conducted to ensure compliance with regulatory standards, protect human health, and preserve aquatic ecosystems.
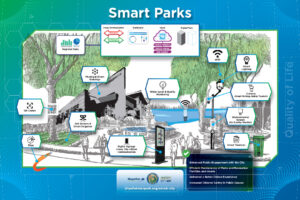
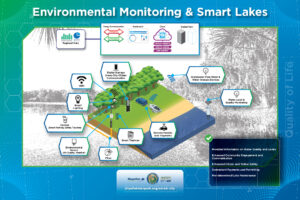
The goal of this pillar is to improve the quality, sustainability and aesthetics of the city’s environment in order to create a healthier, more beautiful place to live, work, and play for today’s residents and future generations.
= The city has implemented some of these features.
= The city will consider implementing these features.
- City-Citizen Communication
City-citizen communication refers to the exchange of information, feedback, and ideas between municipal governments or city authorities and the residents of a city. It involves various channels and methods used to facilitate communication, engage citizens, and promote transparency and collaboration in urban governance. - Digital Signage
Digital signage refers to the use of digital displays to convey information, advertising, or multimedia content in public spaces. It is a dynamic and interactive form of signage that allows for real-time updates and targeted messaging. - Environmental Sensors
Sensors that monitor and communicate any number of environmental parameters or metrics for real-time and analytical purposes. - Fiber Network
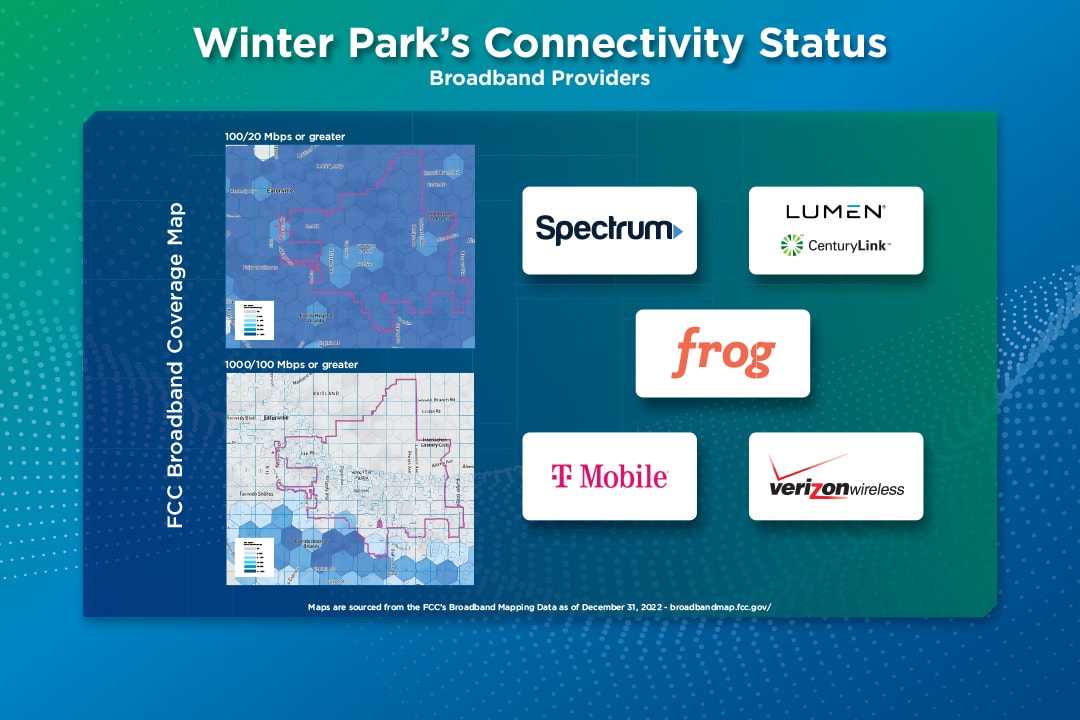
A fiber network provides the foundation for secure connectivity and bandwidth for network communications. - Public Wi-Fi
Wireless internet access that is provided in public spaces, allowing individuals to connect their smart devices without the need for a wired connection. - QR Codes
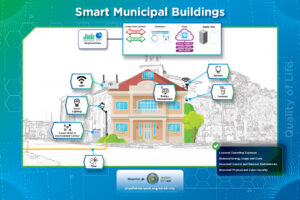
Short for Quick Response codes, QR codes are two-dimensional barcodes that contain information that can be scanned and read using a QR code reader or a smartphone camera. - Smart Municipal Buildings
Smart municipal buildings refer to government-owned or operated facilities that incorporate advanced technologies and data-driven solutions to optimize energy efficiency, enhance operational performance, improve sustainability, and provide a better experience for occupants and visitors. - Smart Trashcan
A smart trashcan, also known as an intelligent waste bin or smart waste management system, refers to a garbage container that incorporates advanced technologies to optimize waste collection and management processes. - Soil Sensors & Smart Irrigation
Soil sensors and smart irrigation systems are components of an intelligent landscaping approach that leverages technology to optimize water usage and promote efficient plant growth, reducing water waste and improving overall irrigation efficiency. - Wayfinding
Wayfinding refers to the process of navigating and orienting oneself within an environment, such as a building, campus, or city, by using visual cues, signage, maps, and other informational resources.
Infrastructure
Digital infrastructure refers to the foundational technology components and systems that enable the functioning of digital networks, services, and applications. It encompasses a wide range of elements, including hardware, software, networks, data centers, and communication systems.
= The city has implemented some of these features.
= The city will consider implementing these features.
- Drone Integration
Drone integration refers to the incorporation of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), commonly known as drones, into existing systems, processes, and industries to enhance operations and provide new services. Drone integration involves the seamless integration of drones with other technologies, regulations, and workflows to ensure safe and efficient operations. - Fiber Network
A fiber network provides the foundation for secure connectivity and bandwidth for network communications. - Public Wi-Fi
Wireless internet access that is provided in public spaces, allowing individuals to connect their smart devices without the need for a wired connection. - QR codes
Short for Quick Response codes, QR codes are two-dimensional barcodes that contain information that can be scanned and read using a QR code reader or a smartphone camera.
A smart city is an urban area that leverages technology and data-driven solutions to improve the quality of life for its residents, enhance sustainability, and optimize resource utilization.
= The city has implemented some of these features.
= The city will consider implementing these features.
- Body Cameras
Body cameras are small recording devices typically worn by law enforcement officers or other professionals to capture audio and video footage of their interactions. Body cameras are designed to provide an objective record of events and enhance transparency, accountability, and trust in public safety operations. - City-Citizen Communication
City-citizen communication refers to the exchange of information, feedback, and ideas between municipal governments or city authorities and the residents of a city. It involves various channels and methods used to facilitate communication, engage citizens, and promote transparency and collaboration in urban governance. - Dash Cameras
Dash cameras are deployed on vehicles to improve situational awareness, after-incident documentation, and transparency. - Digital Signage
Digital signage refers to the use of digital displays to convey information, advertising, or multimedia content in public spaces. It is a dynamic and interactive form of signage that allows for real-time updates and targeted messaging. - Drone Integration
Drone integration refers to the incorporation of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), commonly known as drones, into existing systems, processes, and industries to enhance operations and provide new services. Drone integration involves the seamless integration of drones with other technologies, regulations, and workflows to ensure safe and efficient operations. - Environmental Sensors
Sensors that monitor and communicate any number of environmental parameters or metrics for real-time and analytical purposes. - Public Cameras
Public cameras have many uses including smart traffic, smart parking and public safety while being respectful of citizens’ rights to privacy. - Smart Lighting
Smart lighting refers to an intelligent lighting system that utilizes advanced technologies, such as sensors, wireless connectivity, and automation, to provide enhanced control, energy efficiency, and convenience in lighting applications.
In a smart city, common data refers to the collection, sharing, and analysis of data from various sources within the urban environment. This data comes from sensors, devices, and systems deployed throughout the city’s infrastructure and services. Common data serves as the foundation for implementing smart city solutions and enabling informed decision-making.
= The city has implemented some of these features.
= The city will consider implementing these features.
- Body Cameras
Body cameras are small recording devices typically worn by law enforcement officers or other professionals to capture audio and video footage of their interactions. Body cameras are designed to provide an objective record of events and enhance transparency, accountability, and trust in public safety operations. - City-Citizen Communication
City-citizen communication refers to the exchange of information, feedback, and ideas between municipal governments or city authorities and the residents of a city. It involves various channels and methods used to facilitate communication, engage citizens, and promote transparency and collaboration in urban governance. - Dash Cameras
Dash cameras are deployed on vehicles to improve situational awareness, after-incident documentation, and transparency. - Remote Payments
Financial transactions that are conducted electronically between two parties who are not physically present at the same location. - Smart Curb Management
Smart Curb Management refers to the use of technology and data-driven solutions to optimize and efficiently manage curbside space in urban areas.